This field is found in SSL certificates and TLS certifcates. It is used to specify the identity for the service. This can include domain names, but it's more common for the certificate to also have a subject name alternative (SAN) extensions that indicate which domain names or wildcards the certifies covers. SANs are usually sold separately from single-name SSL certificate standard products and cost more.
SANs can be used to support multiple-domain SSL certificates, where each certificate covers a different domain such as the main website and subdomains. SSL certificates contain a key in addition to CN and SAN. This key is used for digital signature verification and key encryption.
Common Name Mismatch Error
Browsers display a message stating that "Your connection does not appear private" if CN/SAN values do not match. This error message can be misleading because it could appear as if the server is not configured correctly or that there's a problem with the security certificate of the website.
The most common reason for this error is that the SAN or Common Name of the SSL certificate does not correspond to the host name being accessed. This error can occur when the host being accessed does not appear in the certificate. Or, if that host name has been changed since the certificate was issued.

Certificate signing request common name
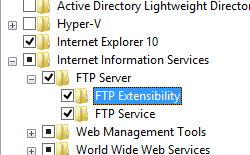
When you create a certificate signing request (CSR), the CSR must include a certificate common name. This can be either an FQDN (fully-qualified domain names) or a 'wildcard' name.
The certificate must be signed by a CA. It can be either a third-party or enterprise CA such as Microsoft's Certification Authority MMC Snap-in.
During the Certificate Signing Request process, the CSR can be submitted to a CA with a user-provided private key in the form of an uploaded file. The CA is responsible for verifying the information submitted by you and signing the certificate.
On this page, you can edit the common name included in your SSL or TLS certificate. You can change the Common Name on either a regular SSL certificate (or deluxe SSL) and must select a name that does not appear in your certificate.
Certificate Authority Common Title
The common name of a certificate authority is an identifier unique to the CA who signed the certificate. The CA is usually a specific computer, but sometimes an individual or organization may use the certificate.
It is possible to include the issuer's full DN in the certificate's Common Name extension and to include serial numbers in the certificate's Issuer Alt Name extension, but only serial numbers are considered to be unique. This is due to the fact that a certificate’s serial number may be the same value as its issuer’s CN. A single certificate, therefore, can have several values for the Issuer DN.
When the issuer’s CN (or empty) is not specified the SAN values of the certificates must be matched against the SHA1 thumbnail of its direct issues. This matching will allow certificate authenticity if it is based on a tree that has a trusted root.
FAQ
What is the cost of creating an ecommerce website?
It all depends on what platform you have and whether or not you hire a freelancer. eCommerce sites typically start at around $1,000.
Once you choose a platform to use, you can expect a payment of anywhere from $500 to $10,000.
Templates are usually not more expensive than $5,000, unless you have a specific purpose. This includes any customizing you do to your brand.
WordPress is a CMS.
The answer is yes. It is called a Content Management System. CMS is a way to manage your website content without having to use an application such Dreamweaver/Frontpage.
The best part about WordPress is that it's free! Hosting is all you need, and it's usually free.
WordPress was originally created to be a blogging platform. But WordPress now offers many more options, such as eCommerce sites or forums, membership websites and portfolios.
WordPress is simple and easy to install. Download the file from their website, and then upload it to your server. After that, you can simply access your domain name with your web browser.
After installing WordPress, you'll need to register for a username and password. Once you have logged in, a dashboard will appear where you can view all of your settings.
From here, you can add pages, posts, images, links, menus, widgets, and plugins. If editing and creating new content is easier for you, skip this step.
However, if you prefer to work with someone else, you can hire a professional web designer to handle the whole process.
How do you create a free website.
It depends on what type of website you want to create. Are you trying to sell products online, create a blog or build a portfolio of websites?
A combination of HyperText Markup Language, Cascading Stil Sheets and HTML can create an essential website. Although HTML and CSS are possible to create a website, most web developers recommend using WYSIWYG editors such as Frontpage or Dreamweaver.
If you don't have experience designing websites, hiring a freelance developer might be the best option. They can help you build a website customized to your needs.
A freelance developer can charge you a flat fee per project or hourly rate. It all depends on how much work they do in a set timeframe.
Some companies charge between $50 and $100 per hour. Larger projects will usually attract higher rates.
Many freelance websites also list open jobs. You can search there before you contact potential developers directly.
How much do web developers make?
The hourly rate for a website you create yourself is $60-$80. But if you want to charge a lot more, you should consider becoming an independent contractor. The hourly rate could be anywhere from $150 to $200
What should I include in my Portfolio?
All these items should be part of your portfolio.
-
You can also see examples of your previous work.
-
Link to your website (if possible).
-
Your blog may have links
-
These are links to social media sites.
-
You can also find links to other designers' portfolios online.
-
Any awards you received.
-
References.
-
Get samples of your works.
-
Links showing how you communicate with clients.
-
You are willing to learn new technologies.
-
Here are some links to show you are flexible.
-
These links show your personality.
-
Videos showing your skills.
Statistics
- Did you know videos can boost organic search traffic to your website by 157%? (wix.com)
- When choosing your website color scheme, a general rule is to limit yourself to three shades: one primary color (60% of the mix), one secondary color (30%), and one accent color (10%). (wix.com)
- The average website user will read about 20% of the text on any given page, so it's crucial to entice them with an appropriate vibe. (websitebuilderexpert.com)
- Studies show that 77% of satisfied customers will recommend your business or service to a friend after having a positive experience. (wix.com)
- It's estimated that chatbots could reduce this by 30%. Gone are the days when chatbots were mere gimmicks – now, they're becoming ever more essential to customer-facing services. (websitebuilderexpert.com)
External Links
How To
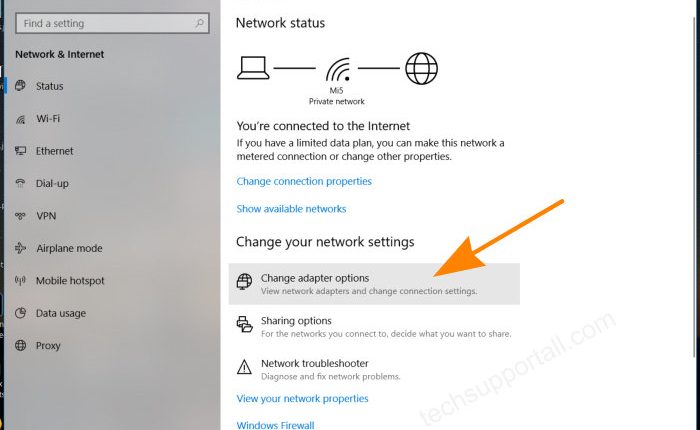
What is Website Hosting?
Website hosting refers to where people go when they visit a website. There are two types:
-
Shared hosting - This is the cheapest option. Your website files reside on a server controlled by someone else. Customers who visit your website send their requests via the Internet over to that server. The request is sent to the server's owner who then passes it on to you.
-
Dedicated hosting - This is the most expensive option. Your website will reside on a single server. Your traffic is private because no other websites have shared space on this server.
Most businesses choose shared hosting because it's less expensive than dedicated hosting. When you use shared hosting, the company that hosts the server gives you the resources to run your site.
However, both have their advantages and disadvantages. These are the key differences between them.
Sharing Hosting Pros
-
Lower Cost
-
Easy To Set Up
-
Regular Updates
-
It can be found on many web hosting companies
You can get shared hosting for as low as $10 per monthly. Remember that shared hosting usually comes with bandwidth. Bandwidth describes the amount of data that can be transferred over the Internet. Even if you are only uploading photos to your blog site, high data transfer rates can still cost you extra.
Once you begin, you will soon see why you spent so much on your previous host. Most shared hosts don't offer any customer support. While they may occasionally assist you in setting up your site and other tasks, after that you are all on your own.
Look for a provider who offers 24/7 phone support. They will help you deal with any issues that arise while your sleeping.
Hosting dedicated:
-
More Expensive
-
Fewer Common
-
Specific Skills Required
With dedicated hosting, all you need to maintain your website are provided. You won’t need to worry whether you have enough bandwidth or enough RAM (random address memory).
This means you'll have to spend more upfront. Once you get started with your online business, you will find that you don't require much technical support. You'll become an expert at managing your servers.
Which Is Better for My Business?
It all depends on the type of website you are creating. If you're selling products only, shared hosting might work best. It is simple to set up and easy to maintain. You'll probably receive frequent updates because you are sharing a server hosting many other sites.
If you are looking to create a community around your brand, dedicated hosting is the best option. It allows you to focus on building your brand and not worrying about managing your traffic.
Bluehost.com has both. They offer unlimited monthly data transfers, 24/7 support, free domain name registration, and a 30-day money-back guarantee.